The Dawn of Quantum Computing: A Revolution in Technology
In the world of technology, few developments hold as much promise and intrigue as quantum computing. Often hailed as the next frontier in computing, quantum computers are poised to solve problems that are currently intractable for classical machines. But what exactly is quantum computing, and why is it considered revolutionary? Let’s delve into the fundamentals, potential applications, and the challenges shaping this groundbreaking field.
What is Quantum Computing?
At its core, quantum computing leverages the principles of quantum mechanics—a branch of physics that deals with the behavior of particles at the smallest scales. Unlike classical computers, which use bits (0s and 1s) to process information, quantum computers use qubits. A qubit can represent a 0, a 1, or both simultaneously thanks to a phenomenon called superposition.
Another key feature of quantum mechanics is entanglement, where two qubits become linked in such a way that the state of one directly influences the state of the other, even when separated by vast distances. These principles allow quantum computers to perform complex calculations at speeds that are exponentially faster than classical computers for certain tasks.
Why Quantum Computing Matters
Quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize industries by solving problems that are currently beyond the reach of classical computers. Here are some areas where quantum computing is expected to make a significant impact:
Cryptography: Quantum computers could break current encryption standards by efficiently solving mathematical problems like factoring large numbers. This has led to the development of post-quantum cryptography to secure digital communications in the quantum era.
Drug Discovery and Healthcare: Simulating molecular interactions at the quantum level could accelerate drug discovery, enabling the development of new medicines and treatments with unprecedented speed and accuracy.
Optimization Problems: Industries like logistics, finance, and manufacturing face complex optimization challenges. Quantum algorithms can find optimal solutions faster, improving efficiency and reducing costs.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Quantum computing can enhance machine learning algorithms by processing vast datasets more efficiently, leading to faster and more accurate AI models.
Material Science: Quantum simulations can help design advanced materials with properties tailored for specific applications, such as superconductors or lightweight alloys.
Recent Breakthroughs in Quantum Computing
The race to build scalable and reliable quantum computers has seen remarkable progress in recent years.
IBM and Google: Both companies have developed quantum processors with increasing numbers of qubits. In 2019, Google claimed “quantum supremacy,” demonstrating that their quantum computer could solve a problem faster than the world’s fastest supercomputer.
Microsoft and Amazon: These tech giants are exploring quantum computing through cloud platforms like Azure Quantum and Amazon Braket, making quantum resources accessible to developers worldwide.
Quantum Startups: Companies like IonQ, Rigetti, and D-Wave are pushing the boundaries of hardware and software innovations, fostering a vibrant ecosystem.
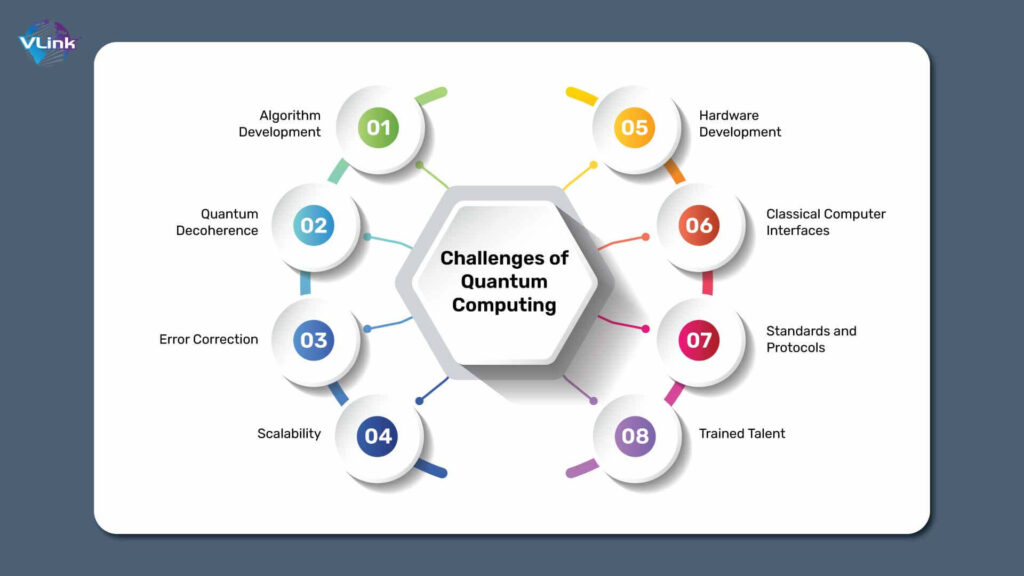
Challenges in Quantum Computing
Despite its potential, quantum computing is still in its infancy, facing several technical and practical hurdles:
Error Correction: Qubits are highly sensitive to environmental disturbances, leading to errors in calculations. Developing effective quantum error correction methods is critical for building reliable quantum systems.
Scalability: Building quantum computers with thousands or millions of qubits remains a significant challenge, as increasing the number of qubits often introduces instability.
Cryogenic Requirements: Most quantum computers operate at near absolute-zero temperatures to maintain qubit coherence, making them expensive and difficult to scale.
Programming Complexity: Quantum programming requires a paradigm shift, with new algorithms and languages tailored for quantum systems, such as Qiskit and Cirq.
What Lies Ahead?
The future of quantum computing is bright, but its journey is still unfolding. Governments and private organizations worldwide are investing heavily in quantum research, recognizing its transformative potential. From national security to global sustainability, quantum computing promises to be a cornerstone of innovation in the decades to come.
As quantum technology matures, it will likely coexist with classical computing, addressing problems that are uniquely suited to its capabilities. The key for businesses and researchers today is to understand the opportunities and prepare for the quantum revolution.
Conclusion
Quantum computing represents a monumental leap forward in our ability to process and analyze information. While challenges remain, the progress so far has been nothing short of extraordinary. As we stand on the cusp of a quantum revolution, the possibilities are as vast as they are exciting. The question is not if quantum computing will change the world, but when.
Stay tuned—the future is quantum.
Want to read more interesting blogs like this……Visit https://www.codersbrain.com/blog/
For Career Opportunities visit : https://www.codersbrain.com/careers/.
